AMSAT NEWS SERVICE
ANS-154
In this edition:
* Last Remaining CubeSatSim Kits Available in AMSAT Store
* Setting Up Your Own Satellite Ground Station with SatNOGS
* SpaceX Aims for Successful Reentry in Fourth Starship Test Flight
* GridMasterMap Satellite Top 100 Rovers June 2024 Rankings
* Changes to AMSAT-NA TLE Distribution for May 31, 2024
* ARISS News
* Upcoming Satellite Operations
* Hamfests, Conventions, Maker Faires, and Other Events
* Satellite Shorts From All Over
The AMSAT News Service bulletins are a free, weekly news and information service of AMSAT, the Radio Amateur Satellite Corporation. ANS publishes news related to Amateur Radio in Space including reports on
the activities of a worldwide group of Amateur Radio operators who share an active interest in designing, building, launching and communicating through analog and digital Amateur Radio satellites.
The news feed on
https://www.amsat.org publishes news of Amateur Radio in Space as soon as our volunteers can post it.
Please send any amateur satellite news or reports to: ans-editor [at] amsat.org
You can sign up for free e-mail delivery of the AMSAT News Service Bulletins via the ANS List; to join this list see:
https://mailman.amsat.org/postorius/lists/ans.amsat.org/
ANS-154 AMSAT News Service Weekly Bulletins
To: All RADIO AMATEURS
From: Radio Amateur Satellite Corporation
712 H Street NE, Suite 1653
Washington, DC 20002
DATE 2024 Jun 02
Last Remaining CubeSatSim Kits Available in AMSAT Store
The final batch of CubeSatSim Kits
are now available for purchase have completely sold out in the AMSAT Store. As of Saturday, June 1 at 1600 UTC, these kits
are on sale were on sale for $400, including shipping to U.S. addresses. Offering a hands-on experience, the CubeSatSim Kit requires minimal soldering and assembly, making it accessible for both educational and public demonstration purposes. Watch for
announcements of future availability of the CubeSatSim Kits from AMSAT.
Editor�??s Note: The last available CubeSatSim Kit was purchased around 1815 UTC on Saturday June 1st. Article was left in this week�??s ANS to share updated information on the
CubeSatSim project.
The CubeSatSim Kit includes:
-
Fully assembled and tested PCBs (STEM Payload, Solar, and Battery Boards)
-
Raspberry Pi Zero WH with a Pi Camera and fully programmed micro-SD card, along with a fully programmed Raspberry Pi Pico WH
-
AMSAT logo Remove Before Flight tag switch
-
3D printed frame, nylon screws, and nuts, with a mini screwdriver included for assembly
-
Metal standoffs, stacking headers, and JST jumpers for stacking the PCBs and Pi Zero WH
-
10 solar panels with JST connectors and mounting tape, requiring minimal soldering
-
BME280 sensor (pressure, temperature, altitude, humidity) and MPU6050 IMU/gyro with male pin headers for easy socket connection
-
Two 6�?� SMA coax cables and two SMA antennas
The kit also comes with an instruction sheet, parts inventory, and links to online instructions. Assembly time is estimated to be under two hours, with a soldering iron, solder, scissors, and the provided mini
screwdriver required.
Limited quantities of the CubeSatSim Kit are now available from the AMSAT Store. [Credit: Alan Johnston, KU2Y]
The latest Beta v1.3 CubeSatSim features improvements over v1.2, such as an FM transceiver, Raspberry Pi Pico microcontroller, and RF command and control. It can also be modified to function as a 500mW high
altitude balloon payload.
For those interested in creating their own CubeSatSim, Beta v1.3 blank PCB sets are available at the AMSAT Store for $35. These require additional components, which can be purchased for approximately $300 using
the provided Bill of Materials.
For detailed updates, visit:
https://www.amsat.org/amsat-cubesatsim-beta-release-v1-3/
Additional resources include:
-
Kit Instructions
https://cubesatsim.org/kit-beta
-
Kit Videos
https://cubesatsim.org/kit-videos-beta
-
Discussion Forum
https://github.com/alanbjohnston/CubeSatSim/discussions
-
Quick Start Guide
https://cubesatsim.org/qsg-beta
For more information or to borrow a loaner CubeSat Simulator, contact Alan Johnston, AMSAT VP Educational Relations, at ku2y [at] arrl.net.
How to Order
Kits will be sold exclusively on the AMSAT Store website.
Only U.S. shipping addresses are eligible; orders with non-U.S. addresses will be refunded and closed.
About CubeSatSim
CubeSatSim is a low-cost satellite emulator powered by solar panels and batteries. It transmits UHF radio telemetry and can be expanded with additional sensors and modules, making it ideal for educational and public demonstrations.
Get Involved
During the beta period, purchasers are encouraged to test the new hardware and software and provide feedback on the instructions and documentation. Past purchasers of the CubeSatSim v1 PCB board sets are eligible for a free upgrade to the v1.3 set of PCB boards
by contacting ku2y [at] arrl.net.
[ANS thanks Alan Johnston, KU2Y, AMSAT Vice President Educational Relations for the above information]
Setting Up Your Own Satellite Ground Station with SatNOGS
Robert Theiss, W5ITR, had the pleasure of interviewing Dan White, AD�?CQ, from the Libre Space Foundation at the 2024 Dayton Hamvention about their innovative SatNOGS project. This initiative enables anyone
to set up a satellite ground station, collect valuable data, and contribute to global satellite operations. You can watch the interview here on the Digital Rancher YouTube channel:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=edNfD_YXZps
Dan explained that SatNOGS provides detailed blueprints and documentation for building a satellite ground station from scratch. The foundation offers the necessary software, identifies accessible hardware,
and maintains the infrastructure that allows citizen scientists to engage in satellite-related sciences. Their vision of making outer space open and accessible through open-source technology is truly inspiring.
Setting up a basic SatNOGS station is surprisingly straightforward. All you need is a Raspberry Pi and an RTL-SDR dongle. Dan explained the process: the Libre Space Foundation provides a ready-to-use image
for the Raspberry Pi, which includes the operating system and necessary configurations. You just create an account, register your station, and schedule a test observation.

Robert Theiss, W5ITR, interviews Dan White, AD�?CQ, with Libre Space at the 2024 Dayton Hamvention. [Credit: Robert Theiss, W5ITR]
For those looking to enhance their setup, SatNOGS offers extensive documentation on building antennas and integrating additional components like low noise amplifiers and band pass filters. Although they plan
to offer kits in the future, you can currently follow the detailed instructions and suggested links available on the SatNOGS Wiki:
https://wiki.satnogs.org.
One of the most fascinating aspects of SatNOGS is its network of interconnected ground stations. Once your station is set up, it can schedule satellite passes and collect data, even while you're asleep. This
data is shared across the network, allowing other users to access it, and vice versa. This system ensures continuous monitoring and data collection, maximizing the utility of each station.
The SatNOGS community is highly active and supportive. The forums on the Libre Space Foundation�??s website are a great resource for troubleshooting, sharing experiences, and staying updated on new satellite
launches and developments.
Dan White, AD�?CQ explains the makeup of their SatNOGS Demonstration Ground Station. [Credit: Robert Theiss, W5ITR]
For those interested in taking their ground station to the next level, SatNOGS supports more advanced setups with full azimuth and elevation rotators and larger antennas. These setups, while more costly, significantly
increase data collection capabilities and overall performance. The Raspberry Pi used in the basic setup can interface with these advanced systems, allowing for automated tracking and data collection.
Dan shared insights into practical aspects such as bandwidth requirements and equipment wear and tear. While the data collected by a SatNOGS station can be bandwidth-intensive, there are settings to optimize
for lower bandwidth situations by disabling audio uploads. Additionally, proper setup and maintenance of antennas and rotators can ensure long-term operation without significant issues.
The Libre Space Foundation and its SatNOGS project provide a unique opportunity for anyone interested in satellite and space communications to get involved. Their open-source approach and comprehensive support
make it accessible even for beginners. Setting up your own satellite ground station is a rewarding experience, contributing to global space exploration and satellite communication. Check out the resources at
https://satnogs.org and get involved!
[ANS thanks Robert Theiss, W5ITR, for the above information]
The 2024 AMSAT President�??s Club coins are here now!
Help Support GOLF and Fox Plus
Join the AMSAT President's Club today and help
Keep Amateur Radio in Space!
https://www.amsat.org/join-the-amsat-presidents-club/
SpaceX Aims for Successful Reentry in Fourth Starship Test Flight
SpaceX is targeting June 6th for the fourth test flight of its Starship megarocket, aiming to demonstrate the rocket�??s ability to survive reentry, according to founder and CEO Elon Musk. This objective marks
a crucial step in proving the reusability of the world's most powerful rocket, following three prior test flights that showcased its capacity to reach space.
On May 20th, SpaceX carried out a crucial test by loading over 10 million pounds of super-cold methane and liquid oxygen propellants into the Super Heavy booster and the Starship upper stage. This practice
countdown, which concluded before engine ignition, was one of the last major tests before the rocket's flight. Following the test, the launch team drained the propellants, and ground crews removed the Starship upper stage to perform additional work on its
heat shield.
The next steps include installing the rocket�??s self-destruct mechanism, to be used if the vehicle deviates off course, and securing a commercial launch license from the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA).
The FAA is reviewing the results of SpaceX's previous Starship test flight in March, which was classified as a mishap after the vehicle lost control and disintegrated during reentry.
SpaceX has requested the FAA approve the upcoming launch before the mishap investigation concludes, arguing that the previous flight did not pose a public safety risk. An FAA spokesperson indicated that this
could expedite the licensing process if no public safety issues are identified.
SpaceX's fourth full-scale Starship rocket underwent a successful fueling test on May 20th. [Credit: SpaceX]
Meanwhile, SpaceX is preparing hardware for multiple rockets scheduled to fly later this year and building additional launch sites in Texas and Florida to support an increased launch frequency. However, significant
design challenges remain before Starship becomes fully operational.
Unlike the March test flight, which included several experiments such as payload bay door operations and liquid oxygen transfer, the upcoming mission will concentrate on controlling the reentry of both the
Super Heavy booster and the Starship upper stage. Both components broke apart during descent in the last flight.
SpaceX aims for the Super Heavy booster, named Booster 11, to achieve a controlled splashdown in the Gulf of Mexico, while the Starship upper stage, known as Ship 29, will attempt to survive the extreme reentry
conditions. The rocket is equipped with about 18,000 hexagonal heat-absorbing ceramic tiles to protect its stainless-steel structure during reentry, where temperatures can reach approximately 2,600°F (1,430°C).
Musk has indicated that, assuming a successful splashdown, SpaceX could attempt landing a Super Heavy booster back at the Texas launch pad as early as the fifth test flight later this year. However, due to
harsher reentry conditions from orbital velocity, landing the Starship upper stage might take longer.
Plasma buildup shown around Starship during Integrated Flight Test 3 on March 14, 2024. [Credit: SpaceX]
NASA, which selected Starship to ferry astronauts to and from the Moon for its Artemis program, is closely monitoring these developments. A critical milestone for NASA is the in-orbit engine restart, necessary
for guiding Starship towards controlled reentry and future lunar missions. While this capability will not be tested on the next flight, achieving reliable engine performance remains a primary focus.
"For us, primarily, it's the successful light of those Raptor engines and achieving main stage with all of them on Booster 11," said Lisa Watson-Morgan, manager of NASA's Human Landing System. The next flight
aims to ensure consistent engine performance, crucial for SpaceX and NASA's lunar ambitions.
Reigniting Raptor engines in space is essential for future missions, but SpaceX is taking a step-by-step approach. "If we can't light all 33 engines on the booster, and if we can't light all six engines on
the ship, then we're going to have trouble getting to where we need to go," Watson-Morgan said. "So it's basically a building-block approach."
As SpaceX prepares for its fourth Starship test flight, the focus on surviving reentry represents a critical hurdle in its mission to develop a fully reusable rocket system capable of reaching, and returning
from, space.
[ANS thanks Stephen Clark, Ars Technica, for the above information]
GridMasterMap Satellite Top 100 Rovers June 2024 Rankings
The June 2024 rankings for the Top 100 Rovers (Mixed LEO/MEO/GEO) in satellite operations, as determined by
@GridMasterMap on Twitter, has been released. The ranking is determined by the number of grids and DXCC entities activated, taking into account only those grids where a minimum number of QSOs logged on the
gridmaster.fr website have been validated by a third party. Grid numbers do not directly reflect the exact number of activations. Satellite operators are encouraged to upload their LoTW satellite contacts to
https://gridmaster.fr in order to provide more accurate data.
Updated: 2024-06-01
|
1 |
ND9M |
26 |
LU5ILA |
51 |
W7WGC |
76 |
FG8OJ |
|
2 |
NJ7H |
27 |
N5BO |
52 |
EA4NF |
77 |
HB9GWJ |
|
3 |
JA9KRO |
28 |
K8BL |
53 |
AA5PK |
78 |
PT9BM |
|
4 |
N5UC |
29 |
KE4AL |
54 |
JL3RNZ |
79 |
DF2ET |
|
5 |
UT1FG |
30 |
DL2GRC |
55 |
SP5XSD |
80 |
KI7UXT |
|
6 |
OE3SEU |
31 |
VE3HLS |
56 |
AD7DB |
81 |
KJ7NDY |
|
7 |
DL6AP |
32 |
KB5FHK |
57 |
F4DXV |
82 |
YU0W |
|
8 |
WI7P |
33 |
KI7UNJ |
58 |
KE9AJ |
83 |
WA9JBQ |
|
9 |
DP0POL |
34 |
LA9XGA |
59 |
KI7QEK |
84 |
N4DCW |
|
10 |
N6UA |
35 |
F4BKV |
60 |
XE1ET |
85 |
KB2YSI |
|
11 |
K5ZM |
36 |
JO2ASQ |
61 |
N8RO |
86 |
N0TEL |
|
12 |
HA3FOK |
37 |
N7AGF |
62 |
KM4LAO |
87 |
N6UTC |
|
13 |
N9IP |
38 |
XE3DX |
63 |
VE1CWJ |
88 |
VE3GOP |
|
14 |
WY7AA |
39 |
PA3GAN |
64 |
SM3NRY |
89 |
JM1CAX |
|
15 |
W5PFG |
40 |
K7TAB |
65 |
N4UFO |
90 |
K0FFY |
|
16 |
AD0DX |
41 |
KE0PBR |
66 |
VA3VGR |
91 |
CU2ZG |
|
17 |
AK8CW |
42 |
KI0KB |
67 |
W1AW |
92 |
KG4AKV |
|
18 |
F5VMJ |
43 |
PR8KW |
68 |
VA7LM |
93 |
VE7PTN |
|
19 |
WD9EWK |
44 |
KE0WPA |
69 |
PT2AP |
94 |
AF5CC |
|
20 |
AD0HJ |
45 |
VK5DG |
70 |
DL4EA |
95 |
VE6WK |
|
21 |
DJ8MS |
46 |
N6DNM |
71 |
M1DDD |
96 |
W8MTB |
|
22 |
ON4AUC |
47 |
EB1AO |
72 |
W8LR |
97 |
K6VHF |
|
23 |
KX9X |
48 |
AC0RA |
73 |
LU4JVE |
98 |
DK9JC |
|
24 |
ND0C |
49 |
JK2XXK |
74 |
AA8CH |
99 |
PT9ST |
|
25 |
KG5CCI |
50 |
N4AKV |
75 |
VE1VOX |
100 |
VO2AC |
[ANS thanks
@GridMasterMap for the above information]
Need new satellite antennas?
Purchase an M2 LEO-Pack from the AMSAT Store!
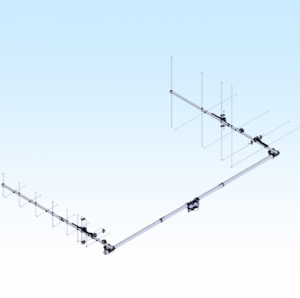
When you purchase through AMSAT, a portion of the proceeds goes towards
Keeping Amateur Radio in Space.
https://amsat.org/product-category/hardware/
Changes to AMSAT-NA TLE Distribution for May 31, 2024
Two Line Elements or TLEs, often referred to as Keplerian elements or keps in the amateur community, are the inputs to the SGP4 standard mathematical model of spacecraft orbits used by most amateur tracking
programs. Weekly updates are completely adequate for most amateur satellites. TLE bulletin files are updated daily in the first hour of the UTC day. New bulletin files will be posted immediately after reliable elements become available for new amateur satellites.
More information may be found at
https://www.amsat.org/keplerian-elements-resources/.
The following satellites have been removed from this week's AMSAT-NA TLE distribution:
+ SO-114 NORAD Cat ID 51081 Decayed from orbit on or about 25 May 2024
+ SO-115 NORAD Cat ID 51080 Decayed from orbit on or about 26 May 2024
+ HODOYOSHI-1 NORAD Cat ID 40299 No Amateur Satellite Service payload
[ANS thanks AMSAT Orbital Elements page for the above information]
ARISS NEWS
Amateurs and others around the world may listen in on contacts between amateurs operating in schools and allowing students to interact with astronauts and cosmonauts aboard the International Space Station.
The downlink frequency on which to listen is 145.800 MHz worldwide.
+ Recently Completed Contacts
Children's Technopark "Quantorium", Obninsk, Russia, direct via TBD
The ISS callsign was RS�?ISS
The scheduled crewmember was Aleksandr Grebyonkin RZ3DSE
The ARISS mentor was RV3DR
Contact was successful Mon 2024-05-27 14:10 UTC
Aznakaevsky district of the Tatarstan Republic, Russia, direct via TBD
The ISS callsign was RS�?ISS
The scheduled crewmember was Aleksandr Grebyonkin RZ3DSE
The ARISS mentor is RV3DR
Contact was successful 2024-05-31 Fri 12:30 UTC
+ Upcoming Contacts
�??Creativity Development Center�?� in Pugachev, Russia, direct via TBD
The ISS callsign is presently scheduled to be RS�?ISS
The scheduled crewmember is Aleksandr Grebyonkin RZ3DSE
The ARISS mentor is RV3DR
Contact is go for 2024-06-03 10:00:00 UTC
Belmont Elementary School, Woodbridge, VA, direct via KM4TAY
The ISS callsign is presently scheduled to be NA1SS
The scheduled crewmember is Jeanette Epps KF5QNU
The ARISS mentor is AA4KN
Contact is go for: Mon 2024-06-03 16:03:00 UTC
Agrupamento de Escolas Dr. Serafim Leite, São João da Madeira, Portugal, direct via CS2ASL
The ISS callsign is presently scheduled to be OR4ISS
The scheduled crewmember is Matthew Dominick KC�?TOR
The ARISS mentor is IK�?USO
Contact is go for: Thu 2024-06-06 10:33:44 UTC
Expect ISS radio outage for Progress 88 docking from May 31st 1720 UTC until June 2nd 1415 UTC. The crossband repeater continues to be active (145.990 MHz up {PL 67} & 437.800 MHz down). If any crewmember is
so inclined, all they have to do is pick up the microphone, raise the volume up, and talk on the crossband repeater. So give a listen, you just never know.
The packet system is also active (145.825 MHz up & down).
As always, if there is an EVA, a docking, or an undocking; the ARISS radios are turned off as part of the safety protocol.
Note, all times are approximate. It is recommended that you do your own orbital prediction or start listening about 10 minutes before the listed time.
The latest information on the operation mode can be found at
https://www.ariss.org/current-status-of-iss-stations.html
The latest list of frequencies in use can be found at
https://www.ariss.org/contact-the-iss.html
[ANS thanks Charlie Sufana, AJ9N, one of the ARISS operation team mentors for the above information]
Upcoming Satellite Operations
G0ABI will activate grid square IN79 from the historic Lizard Wireless Station at Bass Point via GreenCube (IO-117) satellite on June 6th. Lizard Wireless Station is the site where Guglielmo Marconi conducted
his pioneering wireless experiments in 1900. Marconi proved radio communication over the horizon by receiving a transmission from the Isle of Wight in 1901 and later received the first SOS call in 1910. His work at �??The Lizard�?� led to the first transatlantic
radio signal, paving the way for global wireless communication. Celebrate Marconi's legacy by making contact with G0ABI from this iconic location. For more details about the Lizard Wireless Station, visit
https://shorturl.at/DMZ68.
A growing number of satellite rovers are currently engaged in sharing their grid square activations on
https://hams.at. By visiting the website, you gain easy access to comprehensive information about the operators responsible for activating specific grid squares. Additionally, you have the ability to assess the match score between
yourself and a particular rover for a given pass, while also being able to identify the upcoming satellite passes that are accessible from your location.
[ANS thanks Ian Parsons, K5ZM, AMSAT Rover Page Manager, for the above information]
Hamfests, Conventions, Maker Faires, and Other Events
AMSAT Ambassadors provide presentations, demonstrate communicating through amateur satellites, and host information tables at club meetings, hamfests, conventions, maker faires, and other events.
"Moon Day" at the Frontiers of Flight Museum
AMSAT and Amateur Radio satellites will be presented to the general public as part of this annual space themed STEAM event. Volunteers to help at the table space and to do contact demos are welcome. Contact tschuessler [at]
amsat.org for more information.
July 20th, 2024
Dallas Love Field Airport
8008 Herb Kelleher Way
Dallas, TX 75235
https://flightmuseum.com/events/
38th Annual Small Satellite Conference
August 3-8, 2024
Logan, UT, USA
https://smallsat.org
Northeast HamXpostion
August 22-25, 2024
Best Western Royal Plaza Hotel & Trade Center
181 Boston Post Road W
Marlborough, MA 01752
2024 AMSAT Space Symposium and Annual General Meeting
October 25-27, 2024
Doubletree by Hilton Tampa Rocky Point Waterfront
3050 North Rocky Point Drive West
Tampa, FL 33607
[ANS thanks the AMSAT Events page for the above information]
Want to fly the colors on your own grid expedition?
Get an AMSAT car flag and other neat stuff from our Zazzle store!
25% of the purchase price of each product goes towards Keeping Amateur Radio in Space
Keeping Amateur Radio in Space
https://www.zazzle.com/amsat_gear
Satellite Shorts From All Over
+ China's Chang'e 6 probe is set to land on the far side of the moon this weekend, aiming to return lunar samples to Earth. Launched on May 3, the robotic mission entered lunar orbit five days later and is
targeting a touchdown on Saturday night, June 1st, for those in North America. The mission will study its landing area in the South Pole-Aitken Basin, collecting samples over three days before the ascent module returns to lunar orbit. These samples will be
transferred to a return-to-Earth module, with a scheduled Earth landing on June 25. Once returned, the samples will be examined in Beijing and made available to the scientific community for research. This mission builds on the success of Chang'e 5, which returned
61 ounces of lunar material in 2020, and aims to provide insights into the moon's magmatic processes and mantle properties. (ANS thanks Leonard David, Space.com, for the above information)
+ Blue Origin resumed crewed spaceflights on May 19 after a nearly two-year hiatus following a rocket mishap in 2022, which left Virgin Galactic as the sole operator in the suborbital tourism market. Among
the six passengers was Ed Dwight, a former Air Force pilot who had been poised to become NASA's first Black astronaut in the 1960s. Dwight, at 90 years old, became the oldest person to go to space, expressing the profound impact of the experience. Despite
one of the capsule's parachutes failing to fully inflate, the mission was deemed a success, and all passengers returned safely. This flight marks the seventh human mission for Blue Origin, highlighting its ambitions for future space endeavors. The company
has now flown 37 people aboard its New Shepard vehicle, named after the first American in space, Alan Shepard. (ANS thanks Issam Ahmed, Phys.org, for the above information)
+ Rocket Lab successfully launched a small Earth-observation satellite for NASA on May 25, marking the company's 48th liftoff. The Electron rocket lifted off from New Zealand at 3:41 a.m. EDT, carrying the
first of two CubeSats for NASA's PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission. This satellite, deployed into orbit 53 minutes post-launch, will measure heat loss from Earth's polar regions, a critical factor in understanding climate
change. A second PREFIRE satellite will launch within three weeks, with both CubeSats set to operate in 326-mile-high circular orbits. The PREFIRE mission aims to enhance climate models by systematically measuring thermal infrared radiation over the Arctic
and Antarctica. Notably, Rocket Lab's Electron rocket, while designed for reusability, executed this mission without a recovery component. (ANS thanks Mike Wall, Space.com, for the above information)
+Voyager 1 has resumed transmitting science data from two of its four operational instruments after a computer issue arose in November 2023. The mission team is working on recalibrating the remaining two instruments,
with plans to complete this in the coming weeks. This progress follows a five-month troubleshooting effort, during which the spacecraft began sending back usable engineering data. On May 17, commands were successfully sent to the 46-year-old spacecraft, located
over 15 billion miles from Earth, enabling it to resume sending science data. The plasma wave subsystem and magnetometer are now operational, while efforts continue on the cosmic ray subsystem and low energy charged particle instrument. Launched in 1977, Voyager
1 and its twin, Voyager 2, are NASA�??s longest-operating spacecraft and the first to explore beyond the heliosphere, having flown by Jupiter, Saturn, and, in Voyager 2's case, Uranus and Neptune. (ANS thanks NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory for the above information)
Join AMSAT today at
https://launch.amsat.org/
In addition to regular membership, AMSAT offers membership to:
* Societies (a recognized group, clubs or organization).
* Primary and secondary school students are eligible for membership at one-half the standard yearly rate.
* Post-secondary school students enrolled in at least half-time status shall be eligible for the student rate for a maximum of 6 post-secondary years in this status.
* Memberships are available for annual and lifetime terms.
Contact info [at] amsat.org for additional membership information.
73 and remember to help Keep Amateur Radio in Space!
This week's ANS Editor, Mitch Ahrenstorff, AD�?HJ
ad0hj [at] amsat.org





